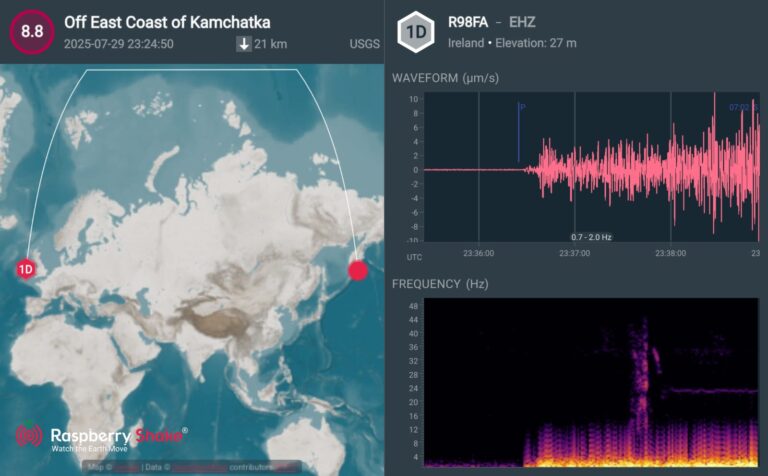
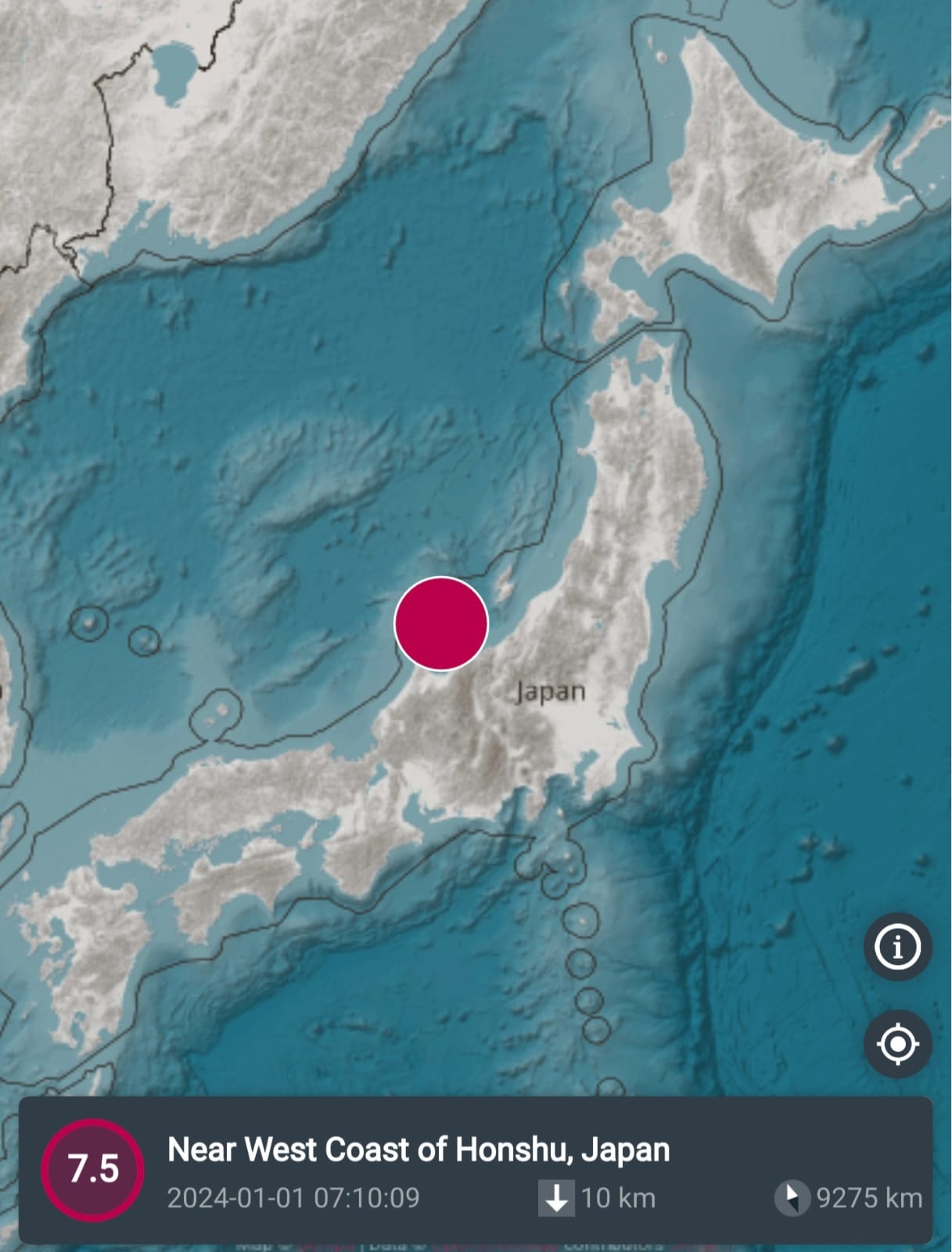
A large M8.8 earthquake occurred July 29th at 23:24 UTC time, offshore east of Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, Russia,. This earthquake occurred as the result of shallow reverse faulting. At the location of this earthquake, the Pacific plate is moving west-northwest with respect to the North America plate at about 80 mm/yr. The North American plate extends westward beyond the North American continent. It is likely this earthquake occurred due to faulting along the subduction zone of the Kuril-Kamchatka arc.
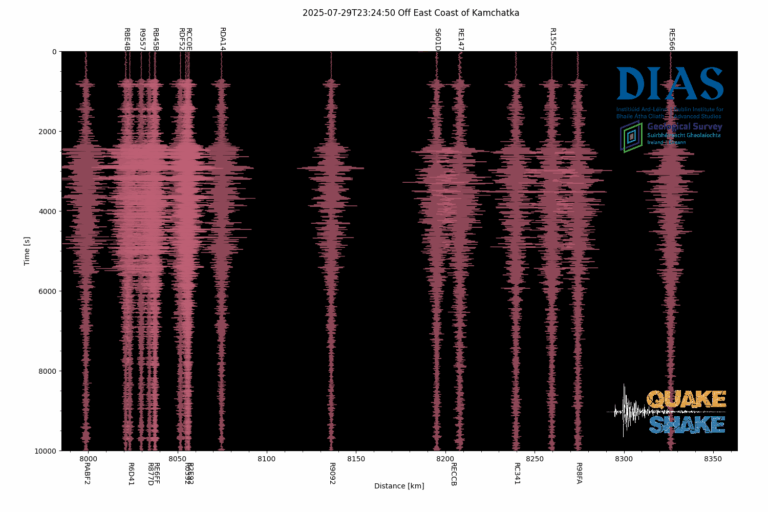
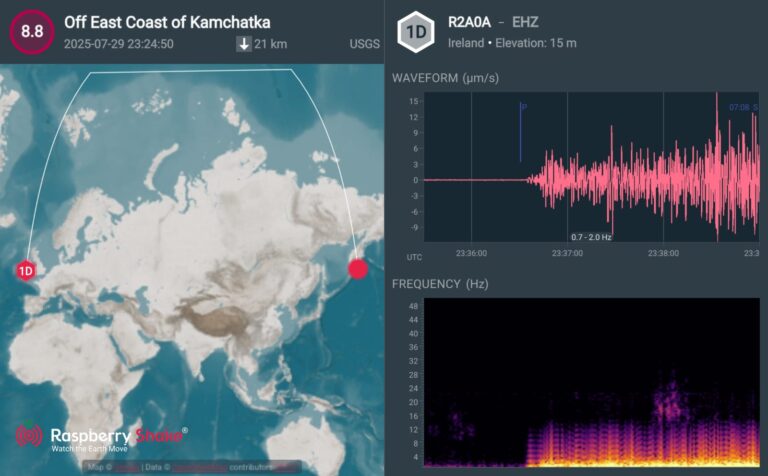
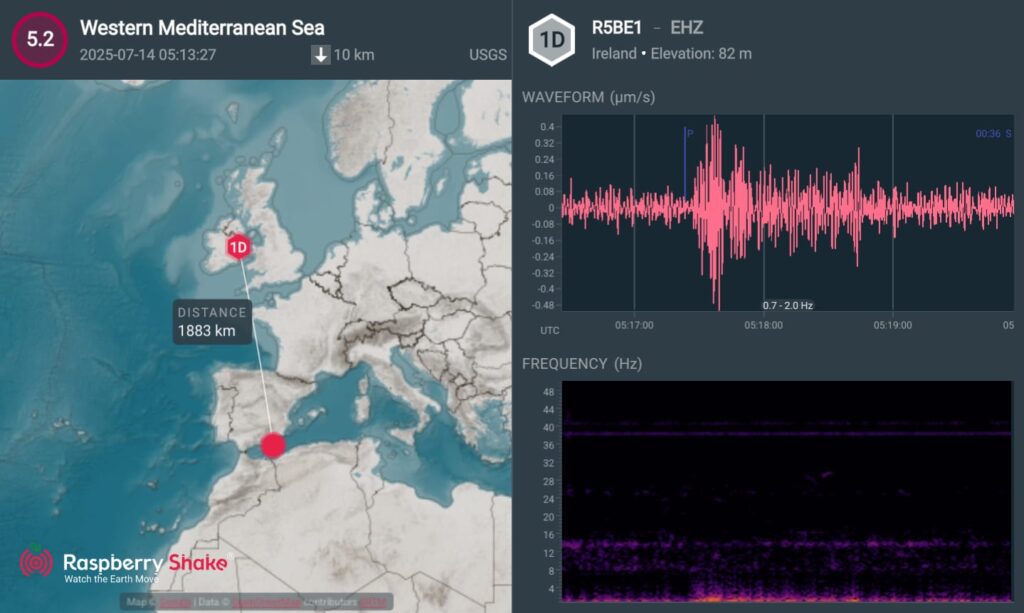
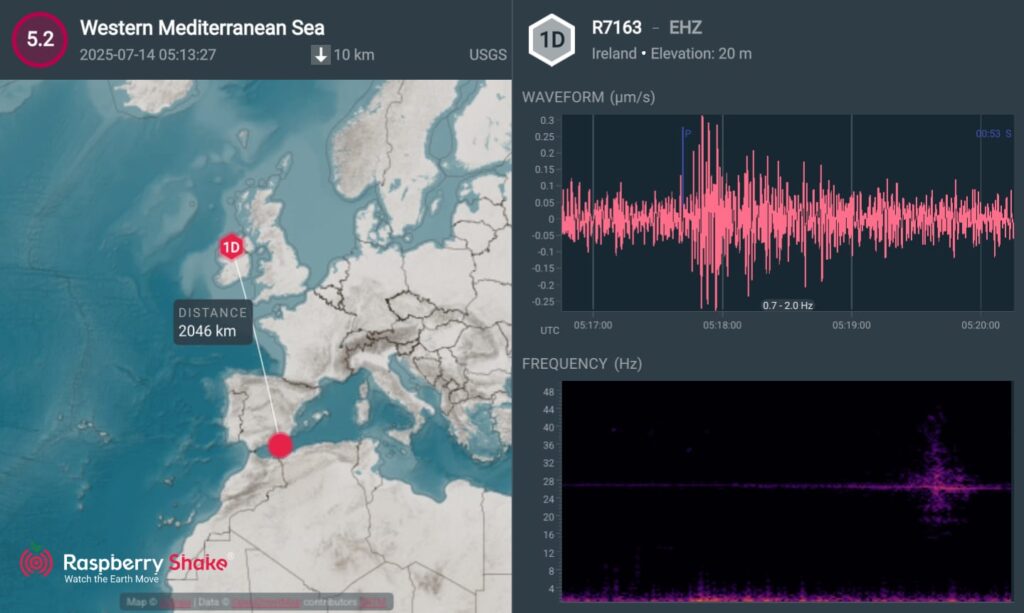
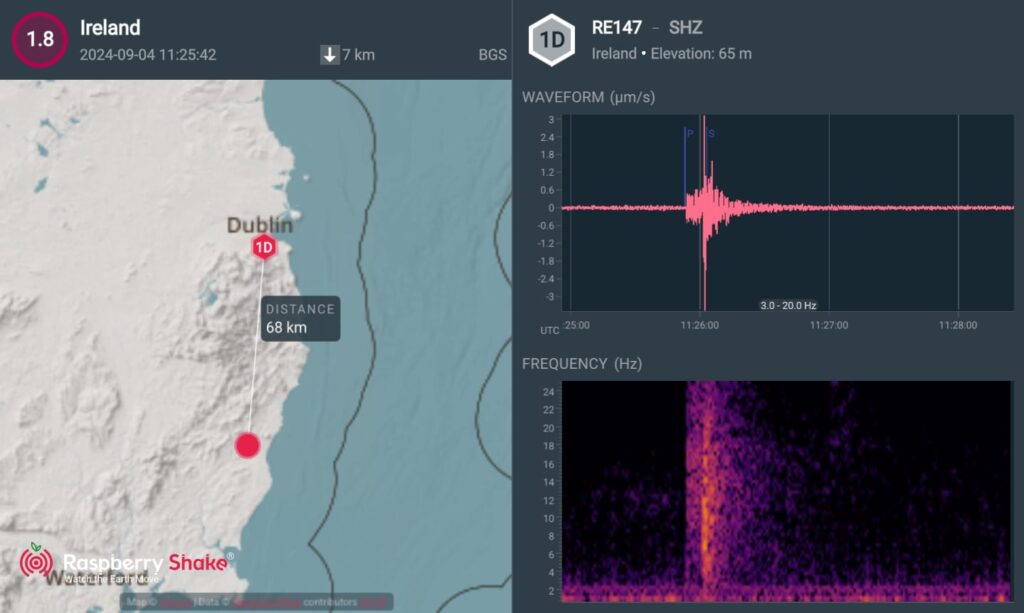
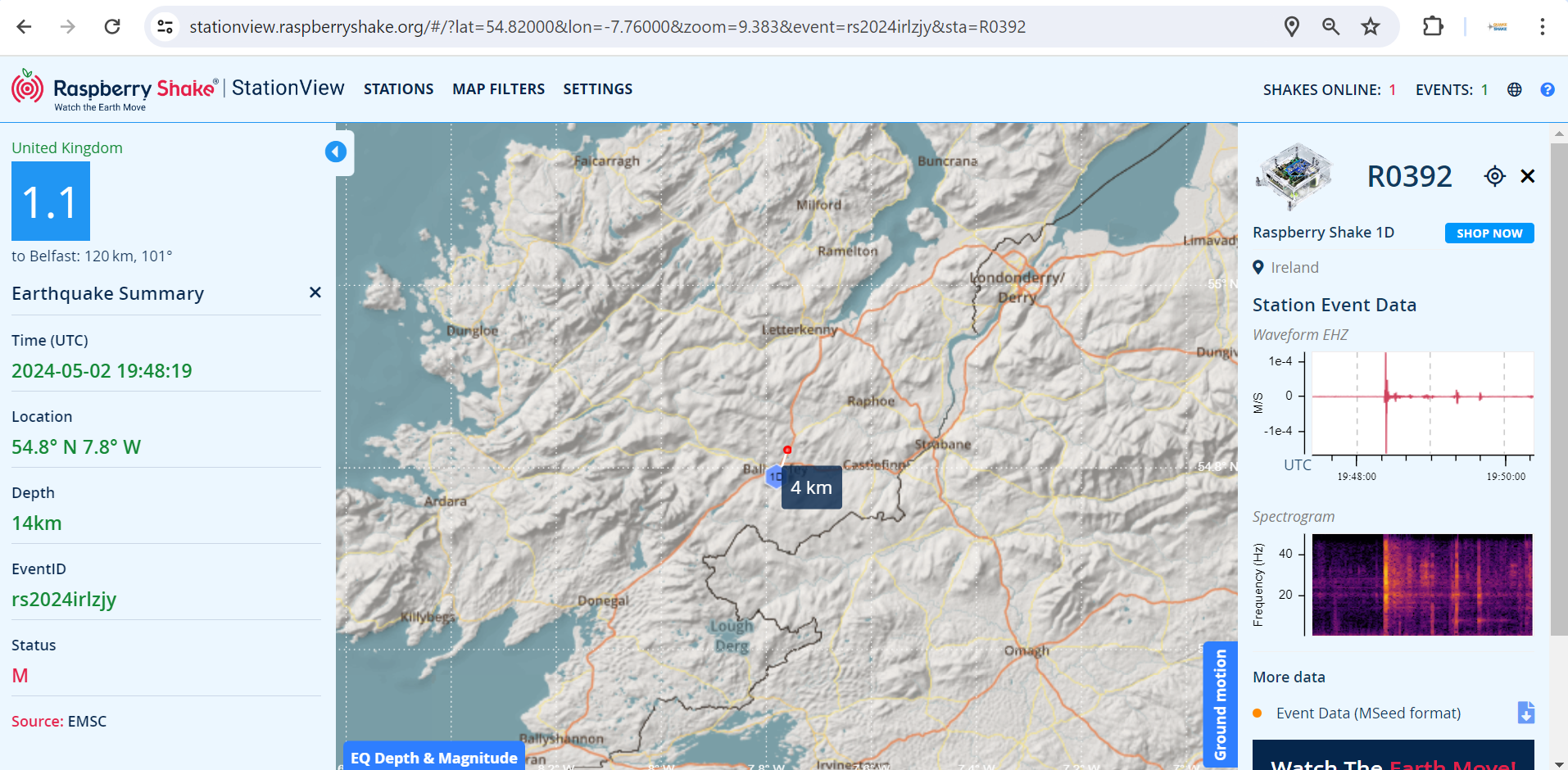
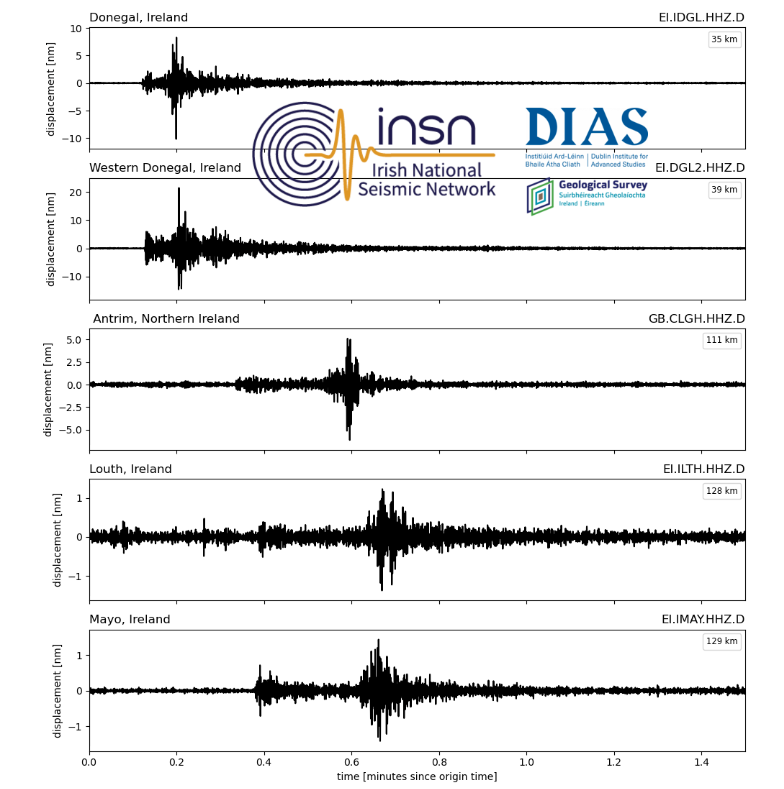
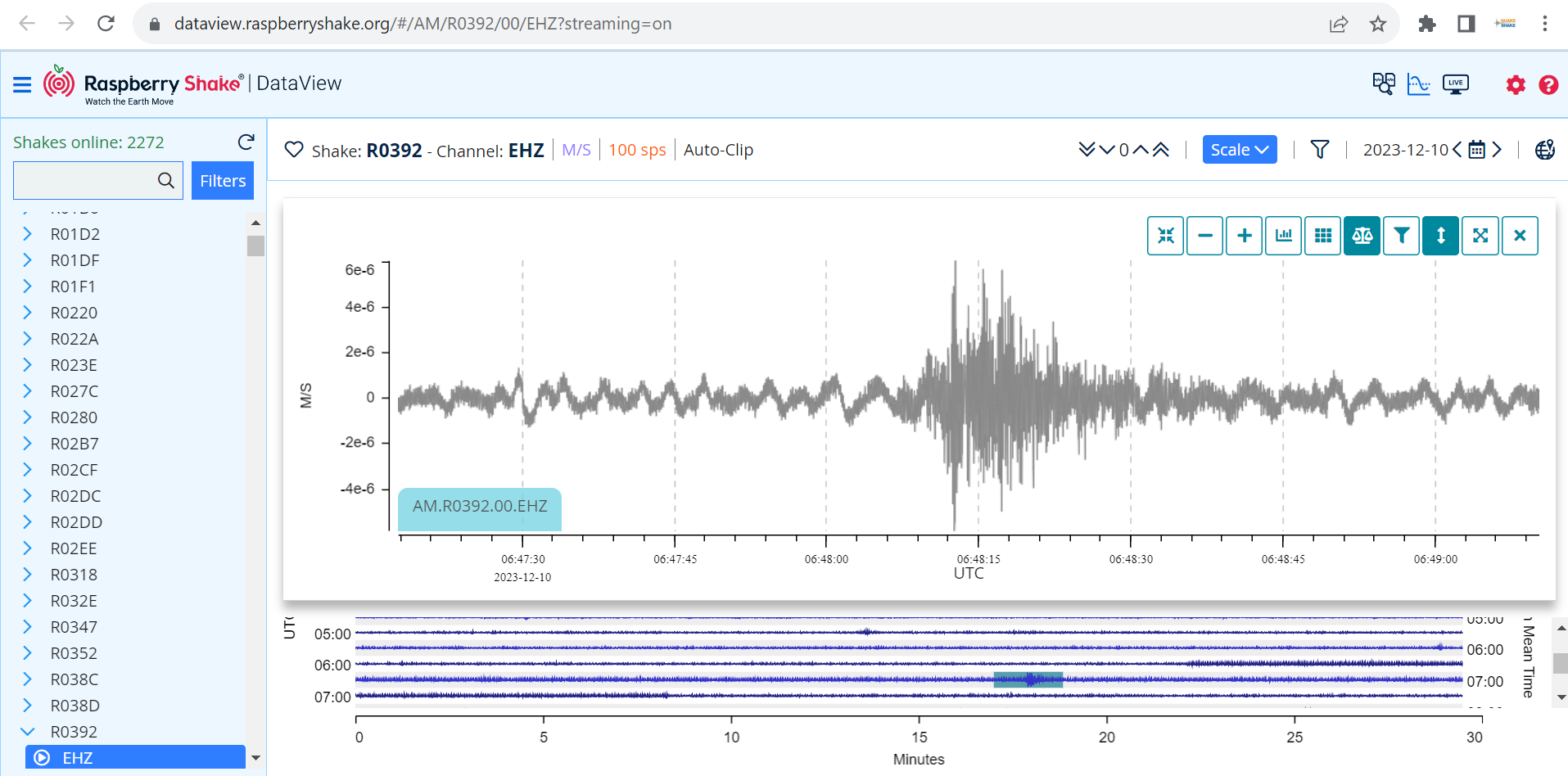
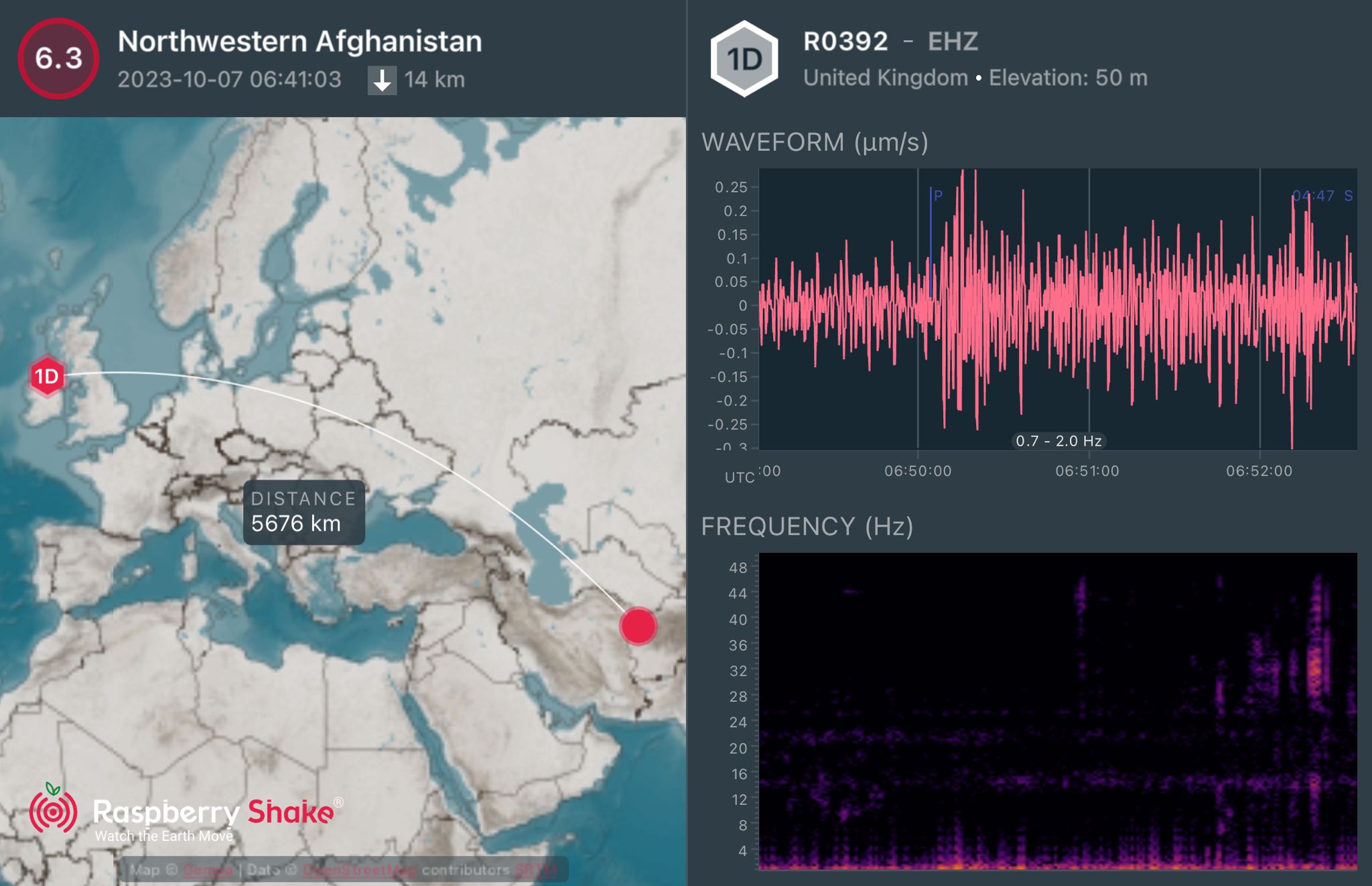
Here is the earthquake recorded by QuakeShake seismometers located thousand of kms away in Ireland (Figure 2.).
Such a large magnitude earthquake will cause slip over a larger fault area spanning kilometers (not just a small point on a map). Reverse faulting events of the size of the July 29, 2025, earthquake are typically about 390 km by 140 km in size.
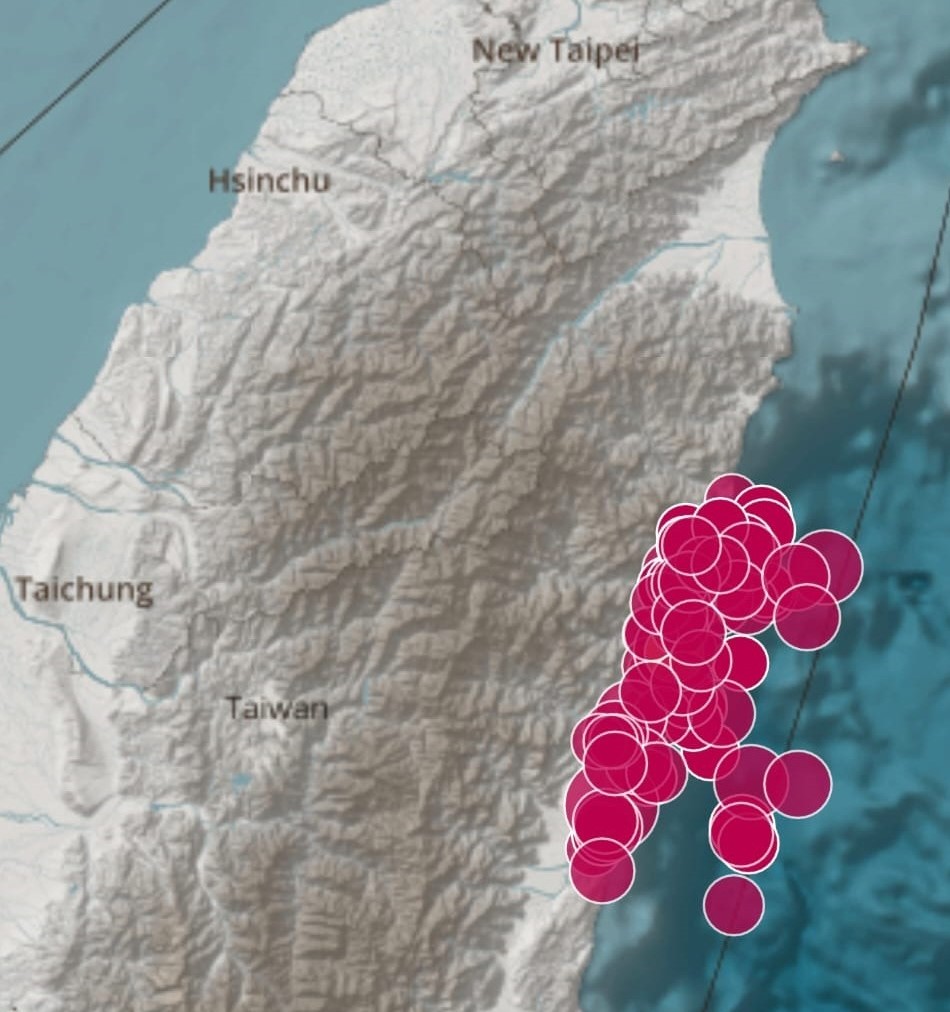
This M8.8 Kamchatka earthquake is the largest worldwide since the 2011 M9.0 Tohoku quake and ranks among the top ten globally since 1900. It follows a sequence of quakes off the Kamchatka Peninsula that began 10 days earlier, including 50 M5.0 plus events, an M7.4 on 20 July, and three M6.6 quakes. As of 4:00 AM UTC on 30 July, 24 aftershocks above M5.0 have been recorded, including M6.9 and 6.3 events.
A tsunami warning has been issued for Japan, Alaska, Hawaii and south toward New Zealand. Residents in low lying areas are being urged to seek higher ground. If you are along the coastline and see water retreating please always move to higher ground as a tsunami may be imminent.
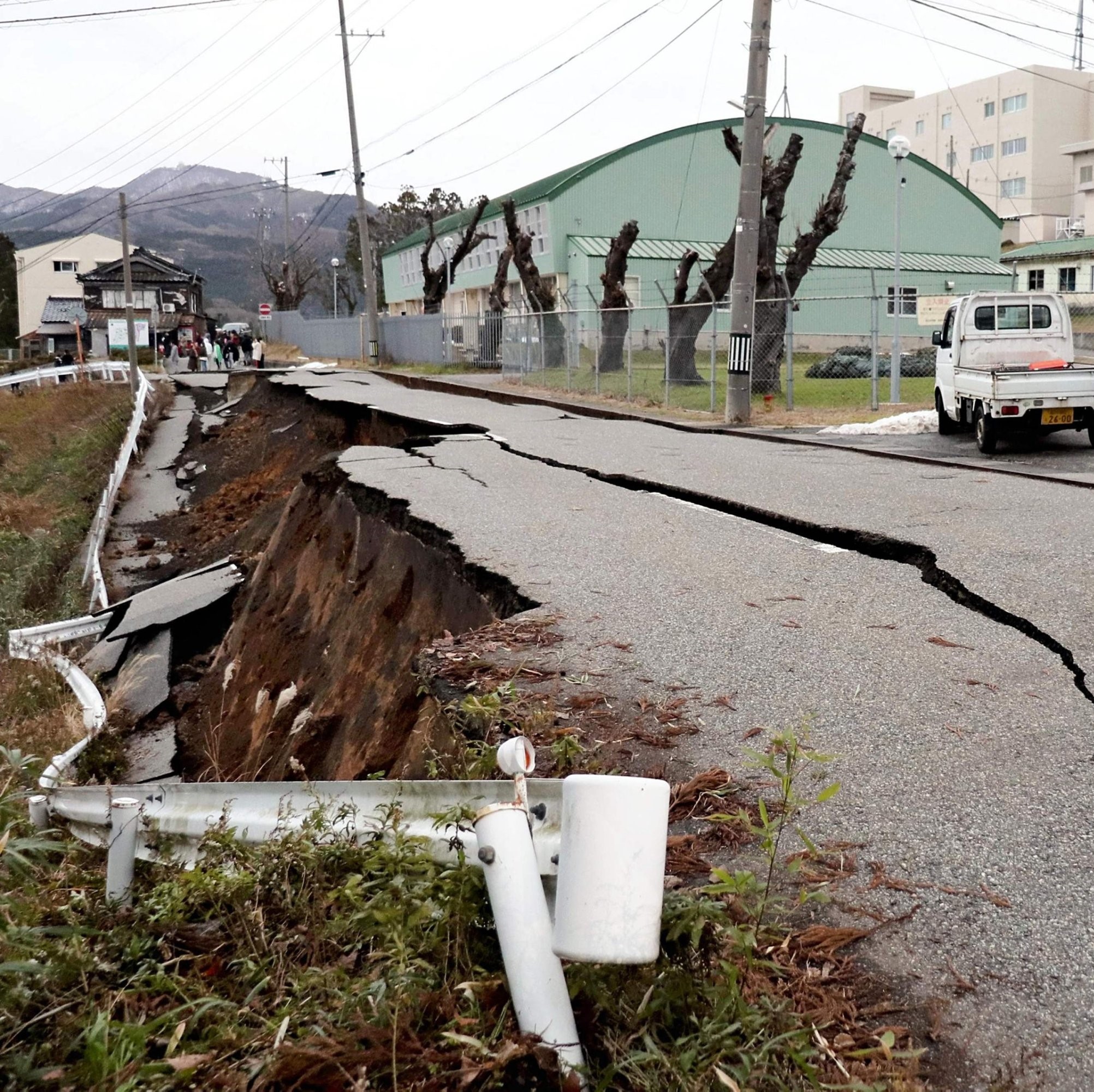
At the time of writing, no casualties have been reported, although there are reports of some injuries and damage to buildings and infrastructure.
A tsunami was generated by this large earthquake with the Pacific Tsunami Warning Center issuing tsunami warnings for parts of Alaska and Hawaii, with waves of up to 1.7m reported in Hawaii.